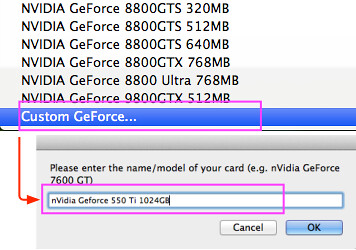
Device (AGP)
{
Name (_ADR, 0x00010000)
Device (VID)
{
Name (_ADR, Zero)
Method (_DOS, 1, NotSerialized)
{
Store (Arg0, MIS4)
SMI (0x9E, MIS4)
}
Method (_DOD, 0, NotSerialized)
{
Store (SMI (0x6D, Zero), Local0)
If (LEqual (Local0, One))
{
Return (Package (0x04)
{
0x00010100,
0x00010200,
0x00010110,
0x00010210
})
}
Else
{
Return (Package (0x04)
{
0x00010100,
0x00010200,
0x00010118,
0x00010120
})
}
}
Device (TV)
{
Method (_ADR, 0, NotSerialized)
{
Return (0x0200)
}
Method (_DCS, 0, NotSerialized)
{
Store (SMI (0x8E, 0x04), Local0)
Return (Local0)
}
Method (_DGS, 0, NotSerialized)
{
Store (SMI (0x99, 0x04), Local0)
Return (Local0)
}
Method (_DSS, 1, NotSerialized)
{
DSS (0x04, Arg0)
}
}
Device (CRT)
{
Method (_ADR, 0, NotSerialized)
{
Return (0x0100)
}
Method (_DCS, 0, NotSerialized)
{
Store (SMI (0x8E, 0x02), Local0)
Return (Local0)
}
Method (_DGS, 0, NotSerialized)
{
Store (SMI (0x99, 0x02), Local0)
Return (Local0)
}
Method (_DSS, 1, NotSerialized)
{
DSS (0x02, Arg0)
}
}
Device (LCD)
{
Method (_ADR, 0, NotSerialized)
{
Store (SMI (0x6D, Zero), Local0)
If (LEqual (Local0, One))
{
Return (0x0110)
}
Else
{
Return (0x0118)
}
}
Method (_DCS, 0, NotSerialized)
{
Store (SMI (0x8E, One), Local0)
Return (Local0)
}
Method (_DGS, 0, NotSerialized)
{
Store (SMI (0x99, One), Local0)
Return (Local0)
}
Method (_DSS, 1, NotSerialized)
{
DSS (One, Arg0)
}
Name (BTVL, 0x64)
Name (DBCL, Package (0x0A) {})
Method (_BCL, 0, NotSerialized)
{
SX10 ()
SX30 (0x19)
SX30 (Zero)
SX11 ()
Store (SX40 (), Index (DBCL, Zero))
Store (SX40 (), Index (DBCL, One))
Store (SX40 (), Index (DBCL, 0x02))
Store (SX40 (), Index (DBCL, 0x03))
Store (SX40 (), Index (DBCL, 0x04))
Store (SX40 (), Index (DBCL, 0x05))
Store (SX40 (), Index (DBCL, 0x06))
Store (SX40 (), Index (DBCL, 0x07))
Store (SX40 (), Index (DBCL, 0x08))
Store (SX40 (), Index (DBCL, 0x09))
SX12 ()
Return (DBCL)
}
Method (_BCM, 1, NotSerialized)
{
SX10 ()
SX30 (0x19)
SX30 (One)
SX30 (Arg0)
Store (Arg0, BTVL)
SX11 ()
SX12 ()
}
Method (_BQC, 0, NotSerialized)
{
SX10 ()
SX30 (0x19)
SX30 (0x02)
SX11 ()
Store (SX40 (), Local0)
Store (Local0, BTVL)
SX12 ()
Return (Local0)
}
}
Device (DVI)
{
Method (_ADR, 0, NotSerialized)
{
Store (SMI (0x6D, Zero), Local0)
If (LEqual (Local0, One))
{
Return (0x0210)
}
Else
{
Return (0x0120)
}
}
Method (_DCS, 0, NotSerialized)
{
Store (SMI (0x8E, 0x08), Local0)
Return (Local0)
}
Method (_DGS, 0, NotSerialized)
{
Store (SMI (0x99, 0x08), Local0)
Return (Local0)
}
Method (_DSS, 1, NotSerialized)
{
DSS (0x08, Arg0)
}
}
Device (GFX0) <------------- Comienzo de nuestro codigo
{
Name (_ADR, Zero)
Name (_SUN, One)
Method (_DSM, 4, NotSerialized)
{
Store (Package (0x1A)
{
"@0,compatible",
Buffer (0x0B)
{
"NVDA,NVMac"
},
"@0,device_type",
Buffer (0x08)
{
"display"
},
"@0,name",
Buffer (0x0F)
{
"NVDA,Display-A"
},
"@1,compatible",
Buffer (0x0B)
{
"NVDA,NVMac"
},
"@1,device_type",
Buffer (0x08)
{
"display"
},
"@1,name",
Buffer (0x0F)
{
"NVDA,Display-B"
},
"NVCAP",
Buffer (0x18)
{
/* 0000 */ 0x04, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x01, 0x00,
/* 0008 */ 0x06, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00,
/* 0010 */ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00
},
"NVPM",
Buffer (0x20)
{
/* 0000 */ 0x01, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00,
/* 0008 */ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00,
/* 0010 */ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00,
/* 0018 */ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00
},
"VRAM,totalsize",
Buffer (0x04)
{
0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x20
},
"device_type",
Buffer (0x0D)
{
"NVDA,GeForce"
},
"model",
Buffer (0x1F)
{
"Nvidia GeForce 8600M GS 256 MB"
},
"rom-revision",
Buffer (0x20)
{
"DSDT ROM v.1a #irc.osx86.es (c)"
},
"reg",
Buffer (0x78)
{
/* 0000 */ 0x00, 0x00, 0x01, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00,
/* 0008 */ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00,
/* 0010 */ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x10, 0x00, 0x01, 0x02,
/* 0018 */ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00,
/* 0020 */ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x01,
/* 0028 */ 0x14, 0x00, 0x01, 0x42, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00,
/* 0030 */ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00,
/* 0038 */ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x10, 0x1C, 0x00, 0x01, 0x02,
/* 0040 */ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00,
/* 0048 */ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x02,
/* 0050 */ 0x24, 0x00, 0x01, 0x01, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00,
/* 0058 */ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00,
/* 0060 */ 0x80, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x30, 0x00, 0x01, 0x02,
/* 0068 */ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00,
/* 0070 */ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x02, 0x00
}
}, Local0)
DTGP (Arg0, Arg1, Arg2, Arg3, RefOf (Local0))
Return (Local0)
}
} <------------- Fin de nuestro codigo (No incluir esta reseña en el DSDT)
}
}